#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
filebuf *pbuf;
ifstream fileStr;
long size;
char *buffer;
//采用二进制模式打开
fileStr.open("D:\Notepad++\notepad2++.exe", ios::binary);
//获取fileStr对应buffer对象的指针
pbuf = fileStr.rdbuf();
// 调用buffer对象方法获取文件大小
size = pbuf->pubseekoff(0, ios::end, ios::in);
pbuf->pubseekpos(0, ios::in);
// 分配内存空间
buffer = new char[size];
// 获取文件内容
pbuf->sgetn(buffer, size);
fileStr.close();
ofstream out("D:\Notepad++\复制.exe",ios::binary);
out.write(buffer, size);
out.close();
delete[]buffer;
return 0;
}
这样写为什么生成的文件比源文件大,不符合PE规范 不能运行。
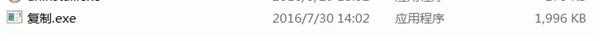
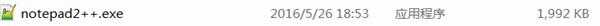
解决方案
20
int main () {
filebuf *pbuf;
ifstream fileStr;
std::streamsize size;
char *buffer;
//采用二进制模式打开
fileStr.open ("C:\Windows\notepad.exe" ,ios::binary);
//获取fileStr对应buffer对象的指针
pbuf = fileStr.rdbuf ();
// 调用buffer对象方法获取文件大小
size = pbuf->pubseekoff (0 ,ios::end);
pbuf->pubseekpos (0 ,fileStr.beg);
// 分配内存空间
buffer = new char[size];
// 获取文件内容
pbuf->sgetn (buffer ,size);
fileStr.close ();
ofstream out ("D:\notepad.exe" ,ios::binary);
out.write (buffer ,size);
out.close ();
delete[]buffer;
return 0;
}




![[小白求帮助]分配的内存什么时候需要手动释放](https://www.codebye.com/wp-content/themes/douth/timthumb.php?src=https://www.codebye.com/wp-content/themes/douth/assets/img/pic/8.jpg&h=110&w=185&q=90&zc=1&ct=1)