定义行为像值的类,写拷贝赋值运算符的时候,用分离式编译分别在has_ptr.h与has_ptr.cpp中
--has_ptr.h--
class HasPtr{
private:
int val;
std::string *ps;
public:
HasPtr(const std::string& arg1 = std::string()) :val(0),ps(new std::string(arg1)){}//构造函数
HasPtr(const HasPtr& other) :val(other.val), ps(new std::string(*other.ps)) {}//拷贝构造函数
HasPtr& operator=(const HasPtr &) ; //拷贝赋值运算符
};
--has_ptr.h--
inline HasPtr& HasPtr::operator=(const HasPtr& other) {
val = other.val;
auto temp = new std::string(*other.ps);//拷贝值,而不是拷贝指针
delete ps;//释放ps原来指向的内存
ps = temp;//temp的域在该拷贝赋值运算符内,该函数调用完成后自动释放
return *this;
} //拷贝赋值运算符
这样的话会显示链接错误:
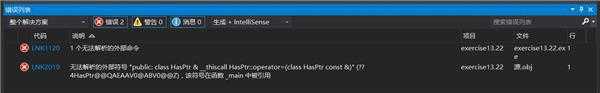
假如把赋值运算符的定义放在头文件,像下面这样,就可以通过了!是什么原因呢?
class HasPtr{
private:
int val;
std::string *ps;
public:
HasPtr(const std::string& arg1 = std::string()) :val(0),ps(new std::string(arg1)){}//构造函数
HasPtr(const HasPtr& other) :val(other.val), ps(new std::string(*other.ps)) {}//拷贝构造函数
HasPtr& operator=(const HasPtr& other) {
val = other.val;
auto temp = new std::string(*other.ps);//拷贝值,而不是拷贝指针
delete ps;//释放ps原来指向的内存
ps = temp;//temp的域在该拷贝赋值运算符内,该函数调用完成后自动释放
return *this;
} //拷贝赋值运算符
};
解决方案
2
去掉 inline 。
10
inline 函数的定义必须在没有使用到它的编译单元中可见。(假如有多个编译单元使用到了这个函数,那么必须在每一个编译单元中可见。即必须在每一个编译单元中均有定义。)
========================================
编译单元可以简单地理解为源文件。
========================================
编译单元可以简单地理解为源文件。
20
原因是内联函数的定义必须出现在被调用之前




![[小白求帮助]分配的内存什么时候需要手动释放](https://www.codebye.com/wp-content/themes/douth/timthumb.php?src=https://www.codebye.com/wp-content/themes/douth/assets/img/pic/11.jpg&h=110&w=185&q=90&zc=1&ct=1)