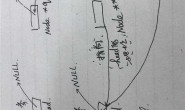
倒序输出,只要写函数就可以啦

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node //结点数据类型
{
char data;
struct node *next;
};
void traverse(struct node* head);
void destroy(struct node* head);
struct node* headinsert(struct node* head);//该函数按照头插法,创建4个结点的动态链表,并返回第1个结点的地址
int main()
{
struct node *head=NULL;
head=headinsert(NULL); //用头插法创建链表
//遍历链表
traverse(head);
//释放资源,销毁链表中全部结点
destroy(head);
}

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node //结点数据类型
{
char data;
struct node *next;
};
void traverse(struct node* head);
void destroy(struct node* head);
struct node* headinsert(struct node* head);//该函数按照头插法,创建4个结点的动态链表,并返回第1个结点的地址
int main()
{
struct node *head=NULL;
head=headinsert(NULL); //用头插法创建链表
//遍历链表
traverse(head);
//释放资源,销毁链表中全部结点
destroy(head);
}
解决方案
40
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node //结点数据类型
{
char data;
struct node *next;
};
void traverse(struct node* head);
void destroy(struct node* head);
struct node* headinsert();//该函数按照头插法,创建4个结点的动态链表,并返回第1个结点的地址
int main()
{
struct node *head=NULL;
head=headinsert(); //用头插法创建链表
//遍历链表
traverse(head);
//释放资源,销毁链表中全部结点
destroy(head);
}
void traverse(struct node* head)
{
struct node *p;
p= head;
while(p)
{
printf("%c ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
void destroy(struct node* head)
{
struct node *p;
while(head)
{
p = head;
head = head ->next;
free(p);
}
}
struct node* headinsert()
{
struct node *p, *head = NULL;
int n=0;
char buffer[64] = {0};
scanf("%s", buffer);
while(buffer[n] != "\0")
{
p = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof(struct node));
p->data = buffer[n];
p->next = head;
head = p;
n++;
}
return head;
}